
Navigating Parenthood With Fertility Awareness In the journey of parenthood, knowledge is power, and fertility awareness provides a valuable tool for couples seeking to plan their pregnancies with intention. Through charting and interpreting fertility signs, such as changes in cervical mucus, basal body temperature, and other secondary fertility indicators, you can identify the fertile window—the period when conception is most likely to occur. By understanding the intricacies of your menstrual cycle, you can identify the days when your fertility is at its peak and plan intimate moments accordingly. Additionally, fertility awareness methods can help identify potential fertility issues or irregularities that may impact conception. By diligently tracking your fertility signs over time, you may gain insights into the length and regularity of your cycles, potentially flagging any abnormalities that warrant further investigation or consultation with a healthcare professional. Moreover, fertility awareness allows you to take a proactive role in optimizing your reproductive health. By nurturing your overall well-being, such as maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress levels, and incorporating self-care practices, you can create an environment conducive to fertility and increase the likelihood of successful conception. As your coach, in this series "Fertility by Design: Navigating Parenthood with Fertility Awareness,", I will be equipping you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions, and empowering you to design your parenthood journey with intention and joy.

Introduction to The Symptothermal Method
It is a comprehensive fertility awareness-based method that combines multiple fertility signs to determine a woman's fertility status throughout her menstrual cycle. It incorporates the observation and tracking of various indicators, including basal body temperature (BBT), cervical mucus, and changes in the cervix.
Here's how the Symptothermal Method works:
1. Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Women using the Symptothermal Method take their basal body temperature every morning before getting out of bed, using a specialized basal thermometer. BBT refers to the body's lowest resting temperature, which slightly increases after ovulation due to the hormone progesterone. By charting BBT over time, a distinct pattern emerges, helping identify the fertile and infertile phases of the menstrual cycle.
2. Cervical Mucus: Observation of cervical mucus is another crucial aspect of the Symptothermal Method. Women track the changes in the characteristics of cervical mucus throughout their cycle, paying attention to factors such as quantity, consistency, and sensation. As ovulation approaches, cervical mucus typically becomes clear, stretchy, and slippery (resembling raw egg whites), indicating increased fertility.
3. Cervical Position and Texture: In addition to cervical mucus, the Symptothermal Method also involves assessing changes in the cervix itself. Women check the position, texture, and opening of the cervix to identify variations that occur throughout the cycle. These changes correspond to different phases of fertility.
Here's an overview of how cervical position can vary throughout the menstrual cycle and its relevance to fertility:
3a. Low and Firm: During most of the menstrual cycle, the cervix is typically positioned low in the vaginal canal and feels firm to the touch. This indicates an infertile phase, particularly when combined with other fertility signs such as non-fertile cervical mucus and basal body temperature (BBT) readings.
3b. High and Soft: As ovulation approaches and fertility increases, the cervix rises higher in the vaginal canal and becomes softer to the touch. The opening of the cervix, may also appear more open or slightly dilated. These changes in cervical position and texture are associated with increased fertility.
3c. Open and High: At the peak of fertility, typically around the time of ovulation, the cervix reaches its highest position, feels soft, and may be more open. This allows sperm to more easily enter the uterus and increases the chances of fertilization.
3d. Low and Firm (Post-Ovulation): After ovulation, the cervix usually returns to a low position, feels firm, and the opening may close partially or completely. These changes indicate the transition to an infertile phase of the menstrual cycle.
ADVANTAGES
The Symptothermal Method offers several advantages as a fertility awareness-based method. Here are some of its key advantages:
1. High Effectiveness: When used correctly and consistently, the Symptothermal Method has been shown to be highly effective for achieving (and avoiding) pregnancy. By combining multiple fertility signs, such as basal body temperature (BBT) and cervical mucus observations, it provides a comprehensive understanding of a woman's fertility, increasing accuracy in determining fertile and infertile phases.
2. Flexibility and Personalization: The Symptothermal Method recognizes that each woman's fertility patterns can vary. It allows for customization and tailoring of the method to suit individual circumstances and preferences. This flexibility empowers women to adapt the method to their unique cycle characteristics and reproductive goals.
3. Natural and Non-Invasive: The Symptothermal Method is a natural and non-invasive approach as it does not involve the use of hormonal interventions or devices (except for the basal body thermometer), making it a desirable option for couples who prefer a more natural and body-aware approach to conception.
4. Enhanced Understanding of Fertility: By actively engaging in the Symptothermal Method, women gain a deeper understanding of their menstrual cycles and fertility patterns. They become more attuned to the changes and signals their bodies provide, fostering a greater sense of body literacy and empowerment.
5. Identification of Potential Health Issues: Regular charting and observation of fertility signs can help identify potential health issues or irregularities that may affect fertility. Abnormalities in basal body temperature patterns, cervical mucus characteristics, or other indicators may prompt further investigation or early detection of certain reproductive health conditions.
6. Partner Involvement: The Symptothermal Method encourages active participation and involvement of both partners. By charting fertility signs and making decisions together, couples can deepen their communication, shared responsibility, and mutual understanding of their reproductive goals.
7. Long-Term Applications: The knowledge gained from practicing the Symptothermal Method can be utilized throughout a woman's reproductive life to track and monitor menstrual health, aid in achieving pregnancy when desired, and provide insights into the natural changes that occur during perimenopause and menopause.
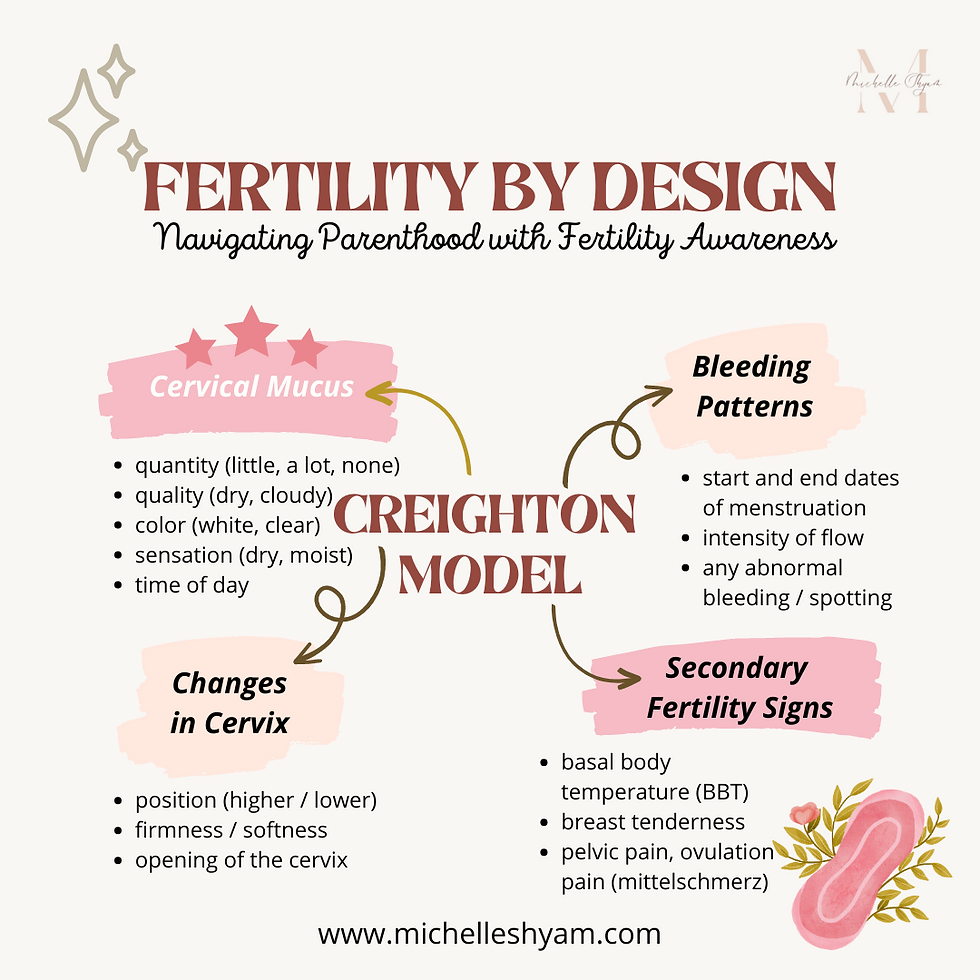
Introduction to the Creighton Model:
- The Creighton Model is a fertility awareness-based method (FABM).
- It was developed by Dr. Thomas Hilgers and his colleagues at the Pope Paul VI Institute for the Study of Human Reproduction.
- The method relies on observing and charting various biological markers to track a woman's menstrual cycle and fertility.
- The primary marker used in the Creighton Model is cervical mucus. Women learn to observe and document changes in the quantity and quality of their cervical mucus throughout the cycle.
- The method also incorporates additional observations, such as bleeding patterns, changes in the cervix, and secondary fertility signs, to provide a comprehensive understanding of a woman's fertility.
- The Creighton Model can be used both to achieve and avoid pregnancy, as it helps identify the fertile and infertile phases of a woman's cycle.
- It can also be utilized to monitor and manage various gynecological conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and hormonal imbalances.
-------
CERVICAL MUCUS
In the Creighton Model, cervical mucus observations play a significant role in understanding a woman's fertility. Here are the key cervical mucus observations made in the Creighton Model:
1. Quantity: Women using this method observe and record the quantity of cervical mucus each day. This includes noting whether there is an absence of mucus or if there is a small, medium, or large amount present.
2. Quality: The quality or characteristics of the cervical mucus are carefully observed and recorded. Women note if the mucus is dry, sticky, creamy, egg white-like (stretchy and slippery), or other variations.
3. Color: The color of the cervical mucus is also observed and documented. It can range from white, yellowish, or clear.
4. Sensation: Women pay attention to the sensation or feeling of the cervical mucus. They note if it is dry, moist, wet, slippery, or lubricative.
5. Time of Day: The time of day when cervical mucus is observed is also recorded. This helps in understanding the changes throughout the menstrual cycle.
BLEEDING PATTERNS: In addition to cervical mucus, the Creighton Model encourages women to observe and record their bleeding patterns throughout the menstrual cycle. This includes noting the start and end dates of menstruation, the intensity of flow, and any abnormal bleeding or spotting. These observations help identify the phases of the cycle and provide insights into hormonal fluctuations.
CHANGES IN CERVIX: The Creighton Model teaches women to monitor changes in the position, firmness, and opening of the cervix. During the fertile phase, the cervix typically becomes higher, softer, more open, and moister to facilitate sperm passage. By tracking these changes, women can gain further information about their fertility status and better understand their reproductive health.
SECONDARY FERTILITY SIGNS: Apart from cervical mucus and cervical changes, the Creighton Model encourages the observation of secondary fertility signs. These signs include changes in basal body temperature (BBT), breast tenderness, pelvic pain, ovulation pain (mittelschmerz), and other physical or emotional symptoms that may be associated with the menstrual cycle. Monitoring these signs provides additional information about hormonal shifts and the timing of ovulation.

Introduction to Billings Method:
- The Billings Ovulation Method is a fertility awareness-based method (FABM) that focuses primarily on observing and charting changes in cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle.
- Women using the Billings Method learn to identify and categorize different types of cervical mucus, such as dry, sticky, creamy, or slippery and the changes in cervical mucus (including sensation) that indicate fertility, particularly the presence of "peak mucus" which signifies the approach of ovulation.
- By tracking and interpreting these cervical mucus changes, women can determine their fertility status and identify the fertile and infertile phases of their cycle.
- The Billings Method can be used both to achieve and avoid pregnancy, as it helps couples make informed decisions about timing intimacy.
- It can also be used to monitor and assess gynecological health, such as identifying irregularities in mucus patterns or detecting potential issues with fertility or hormonal balance.
- The method is natural, non-invasive, and does not require the use of devices or hormones.
HOW IT IS DONE1. Observing Cervical Mucus: In the Billings Ovulation Method, women are taught to observe and assess the characteristics of their cervical mucus throughout the menstrual cycle. This involves checking the vaginal opening and collecting mucus from the cervix using clean fingers.
2. Types of Cervical Mucus: The method categorizes different types of cervical mucus based on their appearance, texture, and sensation. Common categories include dry, sticky, creamy, and slippery or "peak mucus."
3. Dry Phase: During the non-fertile phases of the menstrual cycle, typically following menstruation, women may experience a dry sensation with little or no visible mucus. This indicates a low chance of fertility.
4. Sticky and Creamy Phase: As the cycle progresses, the cervical mucus may transition to a sticky or creamy consistency. This mucus is typically thicker and less conducive to sperm survival, reducing the likelihood of fertility.
5. Peak Mucus: The Billings Method places particular emphasis on identifying "peak mucus," which is the most fertile type of cervical mucus. Peak mucus is clear, stretchy, and slippery, resembling raw egg whites. It signifies the approach of ovulation and the highest likelihood of fertility.
6. Transition to Infertility: After observing peak mucus, women notice a decrease in the quantity and quality of cervical mucus, indicating a transition to the infertile phase of the cycle.
THE ADVANTAGES
1. Continuous Learning: The Billings Method emphasizes continuous learning and understanding of one's own unique mucus patterns. By gaining experience over time, women become more skilled at recognizing and interpreting their cervical mucus observations accurately.
2. Achieving Pregnancy: For couples trying to conceive, the Billings Method can be utilized to identify the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle accurately. By observing changes in cervical mucus, particularly the presence of "peak mucus," women can determine the approaching ovulation. This knowledge enables couples to time intimacy to coincide with the most fertile days, increasing their chances of achieving pregnancy. This method encourages communication and collaboration between spouses, as both are involved in understanding the fertility status.
3. Natural and Non-Invasive: The Billings Method is a natural and non-invasive approach to fertility awareness, as it does not require the use of devices or hormonal interventions. It relies on a woman's own observations of cervical mucus, which is a normal physiological process.
4. Flexibility and Personalization: The Billings Method allows for flexibility and personalization, as it recognizes that each woman's fertility patterns may vary. By gaining experience and understanding their unique mucus observations, women can tailor the method to their individual circumstances and adapt it to their specific fertility goals.

Introduction to The Marquette Method:
The Marquette Method is a fertility awareness-based method (FABM) that incorporates the use of hormonal monitoring through the measurement of urinary hormone levels.
- The primary hormone monitored in the Marquette Method is luteinizing hormone (LH), which surges just before ovulation.
- The method also utilizes the measurement of estrogen metabolites (E3G) to provide additional information about fertility status.
- Women using the Marquette Method typically use a fertility monitor or test strips to measure hormone levels in their urine.
- The Marquette Method can be used both to achieve and avoid pregnancy. It can also be helpful for women with irregular cycles, breastfeeding mothers, and those with certain medical conditions.
- The method requires proper education and training to ensure accurate interpretation of hormone levels and effective use of the method.
How does it work?
In the Marquette Method, the measurement of estrogen metabolites (E3G) is used to provide additional information about fertility status in the following way:
1. Estrogen Metabolites: Estrogen metabolites, specifically E3G (estrone-3-glucuronide), are measured in urine as a marker of estrogen levels in the body. Estrogen plays a crucial role in the menstrual cycle, particularly leading up to ovulation.
2. Urinary Hormone Testing: Women using the Marquette Method typically utilize a fertility monitor or test strips that can detect and measure hormone levels in their urine. These monitors are designed to detect the presence and concentration of E3G.
3. Additional Fertility Information: By measuring E3G levels in urine, the Marquette Method can provide additional information about a woman's fertility status. The rise and fall of estrogen metabolites can indicate the approach of ovulation and help identify the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle.
4. Combined Hormone Monitoring: The Marquette Method combines the measurement of E3G (estrogen metabolites) with the measurement of luteinizing hormone (LH) to provide a more comprehensive picture of fertility. The LH surge typically occurs just before ovulation, and the rise in E3G confirms the presence of estrogen associated with follicle development and the fertile window.
5. Fertility Interpretation: Based on the results of hormone testing, the fertility monitor or test strips used in the Marquette Method provide digital or color-coded readings indicating low, high, or peak fertility. These readings help women determine their fertility status and make informed decisions regarding intercourse timing for pregnancy achievement or avoidance.
6. Personalized Approach: The Marquette Method allows for a personalized approach by considering individual variations in hormone levels and patterns. This can be particularly beneficial for women with irregular cycles or those facing challenges in identifying their fertile window through other methods.
Conclusion:
By incorporating the measurement of estrogen metabolites (E3G) alongside LH monitoring, the Marquette Method aims to provide women with additional fertility information and improve the accuracy of fertility prediction. It is important for women using the Marquette Method to receive proper education, training, and guidance to interpret hormone levels effectively and use the method correctly.
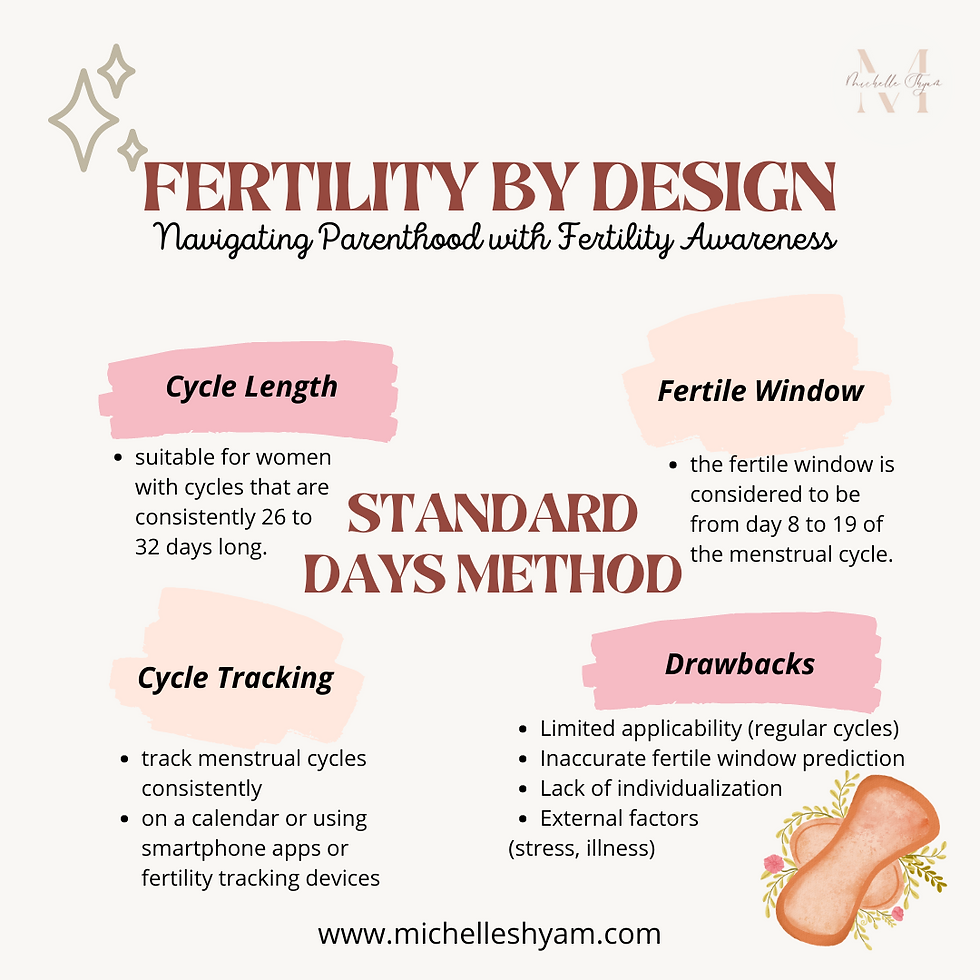
Introduction to The Standard Days Method
It is a fertility awareness-based method (FABM) that relies on tracking menstrual cycle patterns to determine fertility. Here's how the Standard Days Method works:
1. Menstrual Cycle Length: To use the Standard Days Method, a woman needs to have regular menstrual cycles that fall within a specific range. It is suitable for women with cycles that are consistently between 26 and 32 days long.
2. Fertile Window: The method identifies a specific "fertile window" within the menstrual cycle. This is the period when a woman is most likely to conceive and is considered to be from day 8 to day 19 of the menstrual cycle. This assumes that day 1 is the first day of menstrual bleeding.
3. Cycle Tracking: To effectively use the Standard Days Method, it is important for a woman to track her menstrual cycles consistently. This can be done through various methods, such as marking the start and end dates of each menstrual period on a calendar or using smartphone apps or fertility tracking devices.
DRAWBACKS
While the Standard Days Method can be a simple and natural approach to planning pregnancy, it also has certain disadvantages to consider:
1. Limited Applicability: The Standard Days Method is only suitable for women with regular menstrual cycles that consistently fall within the range of 26 to 32 days. Women with irregular cycles or cycles outside of this range may find it challenging to accurately identify their fertile window using this method.
2. Inaccurate Fertile Window Prediction: The method assumes that ovulation occurs on day 14 of the menstrual cycle, which may not be the case for every woman. Ovulation timing can vary from cycle to cycle, even for women with regular cycles. Relying solely on this fixed assumption may result in inaccurately identifying the fertile window and potentially missing the actual fertile days.
3. Lack of Individualized Information: The Standard Days Method does not take into account individual variations in fertility signs or specific indicators of ovulation, such as cervical mucus changes or basal body temperature. It relies solely on the length of the menstrual cycle, which may not provide a comprehensive understanding of a woman's fertility status.
4. External Factors: The Standard Days Method does not consider external factors that can affect fertility, such as stress, illness, travel, or changes in lifestyle. These factors can influence the timing of ovulation and the length of the menstrual cycle, potentially leading to inaccuracies in predicting the fertile window.
It's important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of the Standard Days Method and consider alternative fertility awareness-based methods that may provide more individualized and accurate information about fertility and ovulation.
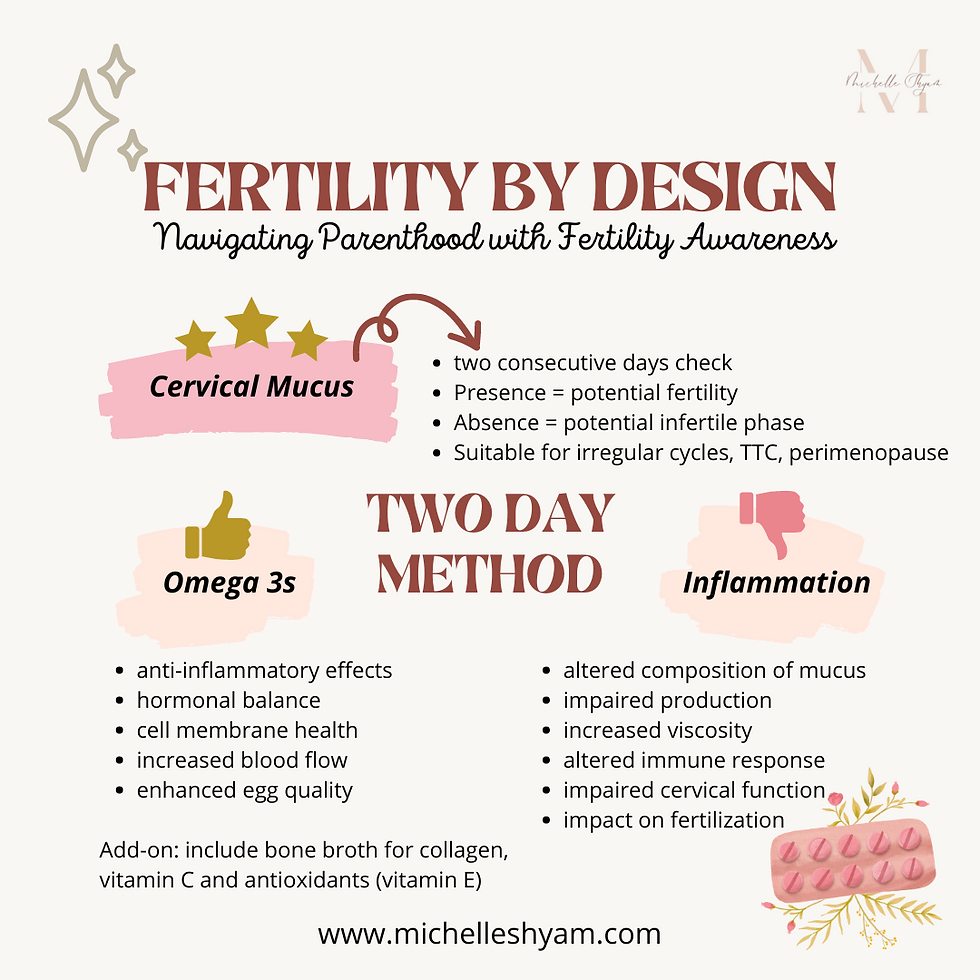
Introduction to The Two-Day Method It is a simplified fertility awareness-based method that can be used to identify the fertile and infertile phases of a woman's menstrual cycle. It relies on observing and recording changes in cervical mucus to determine fertility status. Here's how the Two-Day Method works: 1. Observation of Cervical Mucus: Women using the Two-Day Method pay close attention to the presence or absence of cervical mucus each day. They make a simple binary observation: either there is cervical mucus present or there isn't. 2. Interpretation: The key rule of the Two-Day Method is that if a woman observes any cervical mucus at all on a given day or the previous day, it is considered potentially fertile. This means that intercourse on those days could result in pregnancy. However, if no cervical mucus is observed for two consecutive days, it is considered an infertile phase, and the likelihood of pregnancy is low. 3. Simplicity and Accessibility: The Two-Day Method is a straightforward and accessible fertility awareness method. It does not require detailed charting or monitoring of multiple fertility signs like some other methods. It is particularly suitable for women with irregular cycles or those who find it challenging to consistently observe and interpret other fertility signs. 5. Limitations: While the Two-Day Method can be a useful tool for some women, it has certain limitations. It does not provide as precise information as other methods that track additional fertility signs, such as basal body temperature or changes in the cervix. It also requires women to be vigilant in their daily observations and to accurately differentiate between fertile and infertile mucus. Coming to the most important part or rather what most concerns me - nutrition, for optimal reproductive health! NUTRITION TAKE-AWAYS A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids may contribute to the quality of cervical mucus due to the following reasons: 1. Anti-inflammatory Effects: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation can negatively impact reproductive health, including cervical mucus production and quality. By reducing inflammation, omega-3 fatty acids may help create a more favorable environment for cervical mucus production. 2. Hormonal Balance: Hormonal imbalances can affect the production and consistency of cervical mucus. By promoting hormonal balance, omega-3 fatty acids may help support the production of healthy and fertile cervical mucus. 3. Cell Membrane Health: Omega-3 fatty acids are a key component of cell membranes, including those found in the cervix. Having sufficient omega-3 fatty acids in the diet can help maintain the integrity and fluidity of cell membranes, including the cells responsible for producing cervical mucus. 4. Increased Blood Flow: Omega-3 fatty acids have been associated with improved blood circulation. Adequate blood flow to the reproductive organs, including the cervix, is important for optimal function and mucus production. 5. Enhanced Egg Quality: Omega-3 fatty acids may support overall reproductive health, including the quality of eggs. Healthy eggs are crucial for successful fertilization and implantation. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), walnuts, grass-fed butter into a well-rounded, balanced diet can provide potential benefits for reproductive health. This is where I come in to create a personalized food plan for women based on individual needs and goals. On the other hand, what I do is, give people an anti-inflammatory food plan when achieving and maintaining a healthy pregnancy is important. Inflammation can have a negative impact on the quality of cervical mucus. Here's how inflammation can affect cervical mucus: 1. Altered Composition: Inflammation can disrupt the normal composition of cervical mucus. It may lead to changes in the consistency, texture, and pH balance of the mucus. This can potentially affect its ability to provide an optimal environment for sperm survival and transport. 2. Impaired Production: Inflammatory processes in the reproductive system can interfere with the production of cervical mucus. Inflammation may disrupt the functioning of the cells
responsible for producing and secreting mucus, resulting in reduced mucus production or changes in its quality. 3. Increased Viscosity: Inflammatory conditions can cause cervical mucus to become thicker, stickier, or more viscous. This can hinder the movement and transport of sperm through the cervix, making it more challenging for sperm to reach the fallopian tubes and fertilize an egg. 4. Altered Immune Response: Inflammation can trigger immune responses that may affect cervical mucus quality. An overactive or dysregulated immune response can result in the production of antibodies that target and impact the mucus, potentially making it less conducive to fertility. 5. Impact on Fertilization: Inflammation within the reproductive system can create an environment that is less favorable for fertilization. Changes in the cervical mucus quality caused by inflammation may affect the ability of sperm to survive, swim efficiently, and penetrate the cervical mucus to reach the egg. It's important to note that chronic or persistent inflammation can be indicative of underlying health conditions, such as infections, hormonal imbalances, or autoimmune disorders. Addressing the root cause of inflammation through appropriate medical care and lifestyle adjustments may help improve cervical mucus quality. Consulting with your doctor can provide further guidance and support in managing inflammation and optimizing reproductive health. On my part, I will give you a food plan that is nutrient dense, anti-inflammatory, high on omega 3s, high on vitamin C (this helps in the synthesis of collagen) & vitamin E (which has antioxidative properties). I also tailor your fitness regimen to complement your fertility goals, making sure stress through exercise is low though effective.

Comments